Getting started with Merge Requests
A Merge Request (MR) is the basis of GitLab as a code collaboration and version control.
When working in a Git-based platform, you can use branching strategies to collaborate on code.
A repository is composed by its default branch, which contains the major version of the codebase, from which you create minor branches, also called feature branches, to propose changes to the codebase without introducing them directly into the major version of the codebase.
Branching is especially important when collaborating with others, avoiding changes to be pushed directly to the default branch without prior reviews, tests, and approvals.
When you create a new feature branch, change the files, and push it to GitLab, you have the option to create a Merge Request, which is essentially a request to merge one branch into another.
The branch you added your changes into is called source branch while the branch you'll request to merge your changes into is called target branch.
The target branch can be the default or any other branch, depending on the branching strategies you choose.
In a merge request, beyond visualizing the differences between the original content and your proposed changes, you can execute a significant number of tasks before concluding your work and merging the merge request.
You can watch our GitLab Flow video for a quick overview of working with merge requests.
How to create a merge request
Learn the various ways to create a merge request.
What you can do with merge requests
When you start a new merge request, you'll have the following options to include straightaway (you can also add them later by clicking the Edit button on the merge request's page at the top-right side):
- Assign the merge request to a colleague for review.With GitLab Starter and higher tiers, you can assign it to more than one person at a time.
- Set a milestone to track time-sensitive changes.
- Add labels to help contextualize and filter your merge requests over time.
- Require approval from your team. (STARTER)
- Close issues automatically when it's merged.
- Enable the delete source branch when merge request is accepted option to keep your repository clean.
- Enable the squash commits when merge request is accepted option to combine all the commits into one before merging, thus keep a clean commit history in your repository.
- Set the merge request as a Work In Progress (WIP) to avoid accidental merges before it's ready.
Once you have created the merge request, you can also:
- Discuss your implementation with your team in the merge request thread.
- Perform inline code reviews.
- Add merge request dependencies to restrict it to be merged only when other merge requests have been merged. (PREMIUM)
- Preview continuous integration pipelines on the merge request widget.
- Preview how your changes look directly on your deployed application with Review Apps.
- Allow collaboration on merge requests across forks.
- Perform a Review in order to create multiple comments on a diff and publish them once you're ready. (PREMIUM)
- Add code suggestions to change the content of merge requests directly into merge request threads, and easily apply them to the codebase directly from the UI.
- Add a time estimation and the time spent with that merge request with Time Tracking.
Many of these can be set when pushing changes from the command line, with Git push options.
See also other features associated to merge requests.
Assignee
Choose an assignee to designate someone as the person responsible for the first review of the merge request. Open the drop down box to search for the user you wish to assign, and the merge request will be added to their assigned merge request list.
Multiple assignees (STARTER)
Multiple people often review merge requests at the same time. GitLab allows you to have multiple assignees for merge requests to indicate everyone that is reviewing or accountable for it.
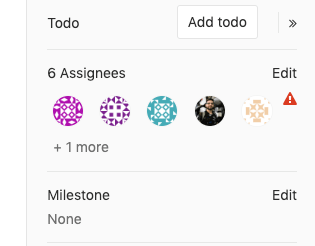
To assign multiple assignees to a merge request:
- From a merge request, expand the right sidebar and locate the Assignees section.
- Click on Edit and from the dropdown menu, select as many users as you want to assign the merge request to.
Similarly, assignees are removed by deselecting them from the same dropdown menu.
It's also possible to manage multiple assignees:
- When creating a merge request.
- Using quick actions.
Merge requests to close issues
If the merge request is being created to resolve an issue, you can add a note in the description which will set it to automatically close the issue when merged.
If the issue is confidential, you may want to use a different workflow for merge requests for confidential issues to prevent confidential information from being exposed.
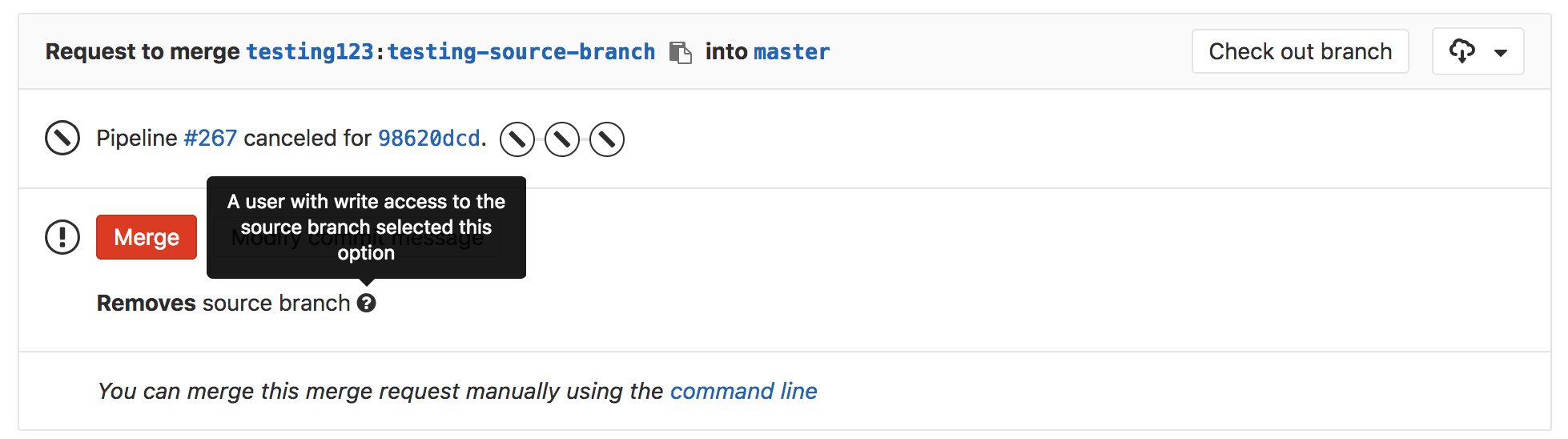
Deleting the source branch
When creating a merge request, select the "Delete source branch when merge request accepted" option and the source branch will be deleted when the merge request is merged. To make this option enabled by default for all new merge requests, enable it in the project's settings.
This option is also visible in an existing merge request next to the merge request button and can be selected/deselected before merging. It's only visible to users with Maintainer permissions in the source project.
If the user viewing the merge request does not have the correct permissions to delete the source branch and the source branch is set for deletion, the merge request widget will show the Deletes source branch text.
Recommendations and best practices for Merge Requests
- When working locally in your branch, add multiple commits and only push when you're done, so GitLab will run only one pipeline for all the commits pushed at once. By doing so, you save pipeline minutes.
- Delete feature branches on merge or after merging them to keep your repository clean.
- Take one thing at a time and ship the smallest changes possible. By doing so, you'll have faster reviews and your changes will be less prone to errors.
- Don't use capital letters nor special chars in branch names.