Subgroups
Introduced in GitLab 9.0.
Subgroups, also known as nested groups or hierarchical groups, allow you to have up to 20 levels of groups.
By using subgroups you can do the following:
- Separate internal / external organizations. Since every group can have its own visibility level, you are able to host groups for different purposes under the same umbrella.
- Organize large projects. For large projects, subgroups makes it potentially easier to separate permissions on parts of the source code.
- Make it easier to manage people and control visibility. Give people different permissions depending on their group membership.
Overview
A group can have many subgroups inside it, and at the same time a group can have only 1 parent group. It resembles a directory behavior or a nested items list:
- Group 1
- Group 1.1
- Group 1.2
- Group 1.2.1
- Group 1.2.2
- Group 1.2.2.1
In a real world example, imagine maintaining a GNU/Linux distribution with the first group being the name of the distribution, and subsequent groups split as follows:
- Organization Group - GNU/Linux distro
- Category Subgroup - Packages
- (project) Package01
- (project) Package02
- Category Subgroup - Software
- (project) Core
- (project) CLI
- (project) Android app
- (project) iOS app
- Category Subgroup - Infra tools
- (project) Ansible playbooks
Another example of GitLab as a company would be the following:
- Organization Group - GitLab
- Category Subgroup - Marketing
- (project) Design
- (project) General
- Category Subgroup - Software
- (project) GitLab CE
- (project) GitLab EE
- (project) Omnibus GitLab
- (project) GitLab Runner
- (project) GitLab Pages daemon
- Category Subgroup - Infra tools
- (project) Chef cookbooks
- Category Subgroup - Executive team
The maximum subgroups a group can have, including the first one in the hierarchy, is 21.
When performing actions such as transferring or importing a project between
subgroups, the behavior is the same as when performing these actions at the
group/project level.
Creating a subgroup
To create a subgroup you must either be an Owner or a Maintainer of the group, depending on the group's setting.
By default, groups created in:
- GitLab 12.2 or later allow both Owners and Maintainers to create subgroups.
- GitLab 12.1 or earlier only allow Owners to create subgroups.
This setting can be for any group by an Owner or Administrator.
For more information check the permissions table. For a list of words that are not allowed to be used as group names see the reserved names.
Users can always create subgroups if they are explicitly added as an Owner (or Maintainer, if that setting is enabled) to a parent group, even if group creation is disabled by an administrator in their settings.
To create a subgroup:
- In the group's dashboard expand the New project split button, select New subgroup and click the New subgroup button.
- Create a new group like you would normally do. Notice that the parent group namespace is fixed under Group path. The visibility level can differ from the parent group.
- Click the Create group button and you will be taken to the new group's dashboard page.
Follow the same process to create any subsequent groups.
Membership
When you add a member to a subgroup, they inherit the membership and permission level from the parent group. This model allows access to nested groups if you have membership in one of its parents.
Jobs for pipelines in subgroups can use Runners registered to the parent group. This means secrets configured for the parent group are available to subgroup jobs.
In addition, maintainers of projects that belong to subgroups can see the details of Runners registered to parent groups.
The group permissions for a member can be changed only by Owners, and only on the Members page of the group the member was added.
You can tell if a member has inherited the permissions from a parent group by looking at the group's Members page.
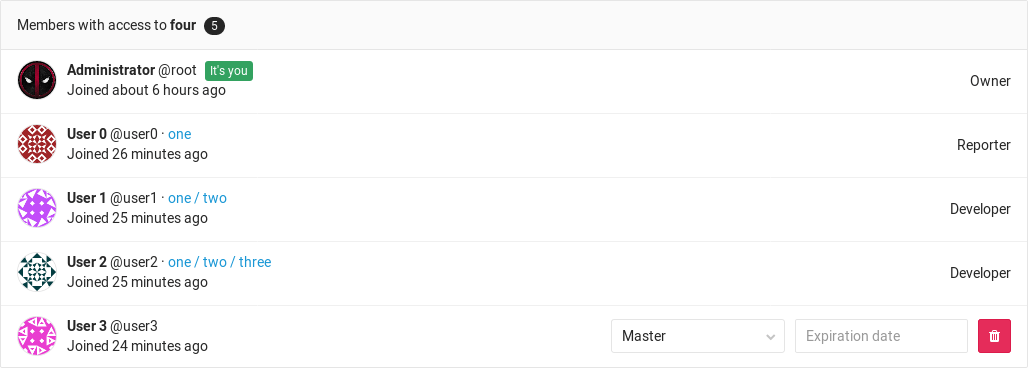
From the image above, we can deduce the following things:
- There are 5 members that have access to the group
four. - User0 is a Reporter and has inherited their permissions from group
onewhich is above the hierarchy of groupfour. - User1 is a Developer and has inherited their permissions from group
one/twowhich is above the hierarchy of groupfour. - User2 is a Developer and has inherited their permissions from group
one/two/threewhich is above the hierarchy of groupfour. - For User3 there is no indication of a parent group, therefore they belong to
group
four, the one we're inspecting. - Administrator is the Owner and member of all subgroups and for that reason, as with User3, there is no indication of an ancestor group.
From GitLab 12.6, you can filter this list using dropdown on the right side:
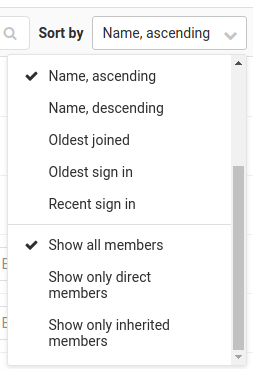
- Show only direct members displays only Administrator and User3, since these are
the only users that belong to group
four, which is the one we're inspecting. - Show only inherited members displays User0, User1 and User2, no matter which group above the hierarchy is the source of inherited permissions.
Overriding the ancestor group membership
NOTE: Note: You must be an Owner of a group to be able to add members to it.
NOTE: Note: A user's permissions in a subgroup cannot be lower than in any of its ancestor groups. Therefore, you cannot reduce a user's permissions in a subgroup with respect to its ancestor groups.
To override a user's membership of an ancestor group (the first group they were added to), add the user to the new subgroup again with a higher set of permissions.
For example, if User0 was first added to group group-1/group-1-1 with Developer
permissions, then they will inherit those permissions in every other subgroup
of group-1/group-1-1. To give them Maintainer access to group-1/group-1-1/group1-1-1,
you would add them again in that group as Maintainer. Removing them from that group,
the permissions will fallback to those of the ancestor group.
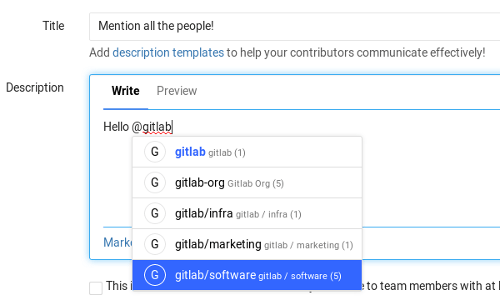
Mentioning subgroups
Mentioning groups (@group) in issues, commits and merge requests, would
notify all members of that group. Now with subgroups, there is more granular
support if you want to split your group's structure. Mentioning works as before
and you can choose the group of people to be notified.
Limitations
Here's a list of what you can't do with subgroups:
- GitLab Pages supports projects hosted under a subgroup, but not subgroup websites. That means that only the highest-level group supports group websites, although you can have project websites under a subgroup.
- It is not possible to share a project with a group that's an ancestor of
the group the project is in. That means you can only share as you walk down
the hierarchy. For example,
group/subgroup01/projectcannot be shared withgroup, but can be shared withgroup/subgroup02orgroup/subgroup01/subgroup03.